In this article: Installing Rspamd on Plesk and Running It in Parallel with Amavis/SpamAssassin
Table of Contents
✨ Motivation
🔹 Repository & Installation
🔹 Basic Configuration
🔹 Secure and Separate Redis Usage
🔹 Connect Postfix in Parallel (without removing Amavis)
🔹 Testing & Web Interface
🔹 SURBL & Whitelist Configuration
🔹 Next Steps
📣 Discussion in the Plesk Forum
✨ Motivation
With increasingly sophisticated spam techniques, traditional antispam systems are reaching their limits. Modern spam campaigns use dynamic content, frequently changing sender infrastructures, and bypass basic heuristic filters. Many mail servers still rely on proven, yet aging systems:
- SpamAssassin, originally released in 2001, uses rule-based filtering with static signatures and external sources like Pyzor, Razor, or DCC. Many servers still use version 3.x, although version 4.x is available.
- Amavis, introduced around 2002, acts as a content filter and middleware between MTAs (e.g., Postfix) and tools like ClamAV and SpamAssassin. Configuration is often managed in complex Perl files like
50-user.
These traditional setups are functional but maintenance-heavy. They require custom tuning with local scores or blacklists to keep up with modern spam waves. Often, they lack Redis support, dynamic learning, and transparency in their decision-making processes.
Rspamd, by contrast, offers a modular, high-performance approach:
- Fast evaluation using C and Lua
- Web interface with live analysis
- Support for Redis, fuzzy hashing, and Bayesian learning
- Integration of SPF, DKIM, DMARC, and SURBL
- Simple multimap rules for blacklists and whitelists
On Plesk servers, a parallel test deployment is a safe first step—allowing comparisons without disrupting the current mail infrastructure. This article explains how to install Rspamd alongside Amavis/SpamAssassin, test it, and integrate a centralized SURBL whitelist.
🔹 Repository & Installation
1. Add Rspamd repository (without [arch=amd64] to avoid i386 warnings on ARM)
# Save GPG key
curl -s https://rspamd.com/apt-stable/gpg.key | gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/rspamd.gpg
# Add repository
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/rspamd.gpg] https://rspamd.com/apt-stable/ $(lsb_release -cs) main" \
| tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/rspamd.list
apt update2. Install Rspamd and Redis
apt install rspamd redis-server redis-tools🔹 Basic Configuration
1. Enable Web Interface
mkdir -p /etc/rspamd/local.d
nano /etc/rspamd/local.d/worker-controller.incContent:
bind_socket = "127.0.0.1:11334";
password = "$2$<hash>"; # generated with `rspamadm pw`
enable_password = true;2. Start Service
systemctl enable rspamd --now🔹 Secure and Separate Redis Usage
Rspamd uses Redis to store fuzzy hashes, Bayes data, and other scores. By default, all data is written to database 0, which can cause conflicts if Redis is also used for Matomo, Drupal, Nextcloud, or other services.
👉 Recommendation:
- Configure Rspamd to use a dedicated Redis database, e.g.,
db = 1 - Secure Redis access with a password
Configuration:
nano /etc/rspamd/local.d/redis.confservers = "127.0.0.1";
password = "your-secret-password";
db = 1;🔐 Set the password in
/etc/redis/redis.conf:
requirepass your-secret-password⚠️ Then restart Redis:
systemctl restart redisThis keeps Rspamd data logically separated from other Redis-backed services.
🔹 Connect Postfix in Parallel (without removing Amavis)
systemctl restart postfix🔐 Important: Do not remove the Milter configured by Plesk (typically used for DKIM/DMARC signing). When adding Rspamd as an additional Milter, simply append it to existing entries.
Example (multiple Milters):
milter_default_action = accept
milter_protocol = 6
smtpd_milters = inet:127.0.0.1:11332, inet:127.0.0.1:12768
non_smtpd_milters = inet:127.0.0.1:11332
milter_mail_macros = i {mail_addr} {client_addr} {client_name} {auth_authen}Here, Plesk’s Milter on port
12768remains active, while11332is added for Rspamd.
⚠️ Rspamd will not block mail—it will only analyze and add headers.
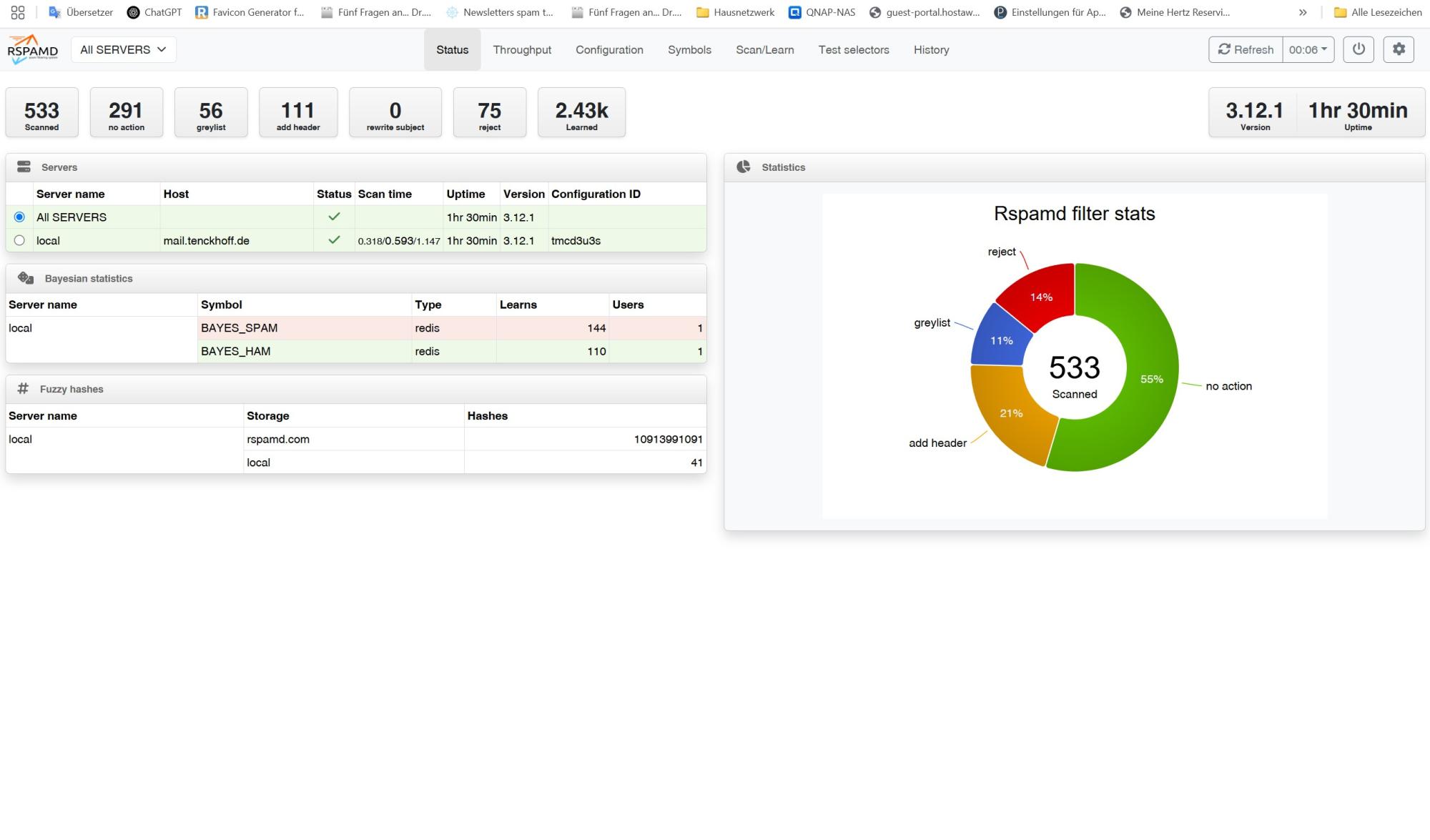
🔹 Testing & Web Interface
- Web UI:
http://localhost:11334 - Logs:
/var/log/rspamd/rspamd.log
Send a test mail:
echo "Test Viagra Spam" | mail -s "Rspamd Test" user@domain.tldCheck headers:
grep -i rspamd /var/mail/<user>🔹 SURBL & Whitelist Configuration (Example)
1. Create a central whitelist file:
nano /etc/rspamd/maps.d/custom_whitelist.mapContents:
lufthansa.com
condor.com
staralliance.com2. Reference it in the SURBL module:
nano /etc/rspamd/local.d/surbl.confwhitelist = "/etc/rspamd/maps.d/custom_whitelist.map";3. Optional: Neutralize false positives
nano /etc/rspamd/local.d/force_actions.confrules {
whitelist_surbl_domains {
expression = "SURBL && from_domain:/etc/rspamd/maps.d/custom_whitelist.map/";
action = "no_action";
description = "SURBL hit but trusted domain";
}
}Now you have a fully functional Rspamd instance running in parallel with Amavis/SpamAssassin on your Plesk test server. It analyzes mails, assigns scores, and offers a web UI—without interfering with your live mail flow.
Next steps:
- Automate whitelist updates (e.g., via cron or GitHub/Gist)
- Train Bayes and fuzzy filters
- Use Redis for mailbox statistics
- Fully migrate by editing
master.cfand disabling Amavis
📣 Discussion and experiences in the Plesk forum: Join the community to share tips or ask questions: 👉 https://talk.plesk.com/threads/migration-from-plesk-email-security-amavis-spamassassin-3-x-to-rspamd-3-12-experiences.378439/#post-962617